AI-Powered Geolocation via Multimedia Content Analysis to Identify Sites of Potential Trafficking Activities: Enhancing Investigations with Cutting-Edge Technology
24 APRIL 2025

In the fight against Trafficking in Human Beings (THB), the early identification of the location of potential victims is crucial for law enforcement efforts, as it enhances their capabilities for quick intervention, timely victim identification and protection, as well as effective disruption of the associated criminal network. The VANGUARD project introduces an innovative Artificial Intelligence (AI)-powered geolocation tool capable of determining the geographic origin of images (both outdoor and indoor) without relying on metadata or geotags. By leveraging advanced AI methods, this tool enables the timely identification of potential locations where individuals may be exploited, ultimately supporting rescue operations.
This work is led by CERTH-ITI-VCL, the Visual Computing Lab of the Information Technologies Institute (ITI) at the Centre for Research and Technology – Hellas (CERTH) in Greece, which develops AI-based tools for multimedia content analysis as part of the project.
AI-based Outdoor Geolocation: Locations Identification through Outdoor Cues
Outdoor geolocation can be challenging as many images lack clear geographic markers. Our AI system analyses various elements, such as text in images, road signs, license plates, and architectural styles to estimate locations. By combining these elements, valuable insights can be provided, allowing investigators to more accurately identify potential trafficking sites. Below, we briefly present the key components of the VANGUARD AI-based Outdoor Geolocation tool.
Scene Recognition for Environmental Context: A deep learning-based model that categorises scenes as urban, rural, coastal, or highway, providing initial contextual information.
License Plate Recognition for Geographic Identification: An AI-powered detection module that identifies vehicle license plates in images, isolating them for further analysis (Figure 1). Optical Character Recognition (OCR) models, including Vision-Language Models (VLLM)-based text extraction, recognise plate characters, which can then be correlated with known license plate formats and country codes to provide indirect location cues.

Figure 1. Licence plate detection
Traffic Sign Detection for Regional Insights: A traffic sign detection module (Figure 2) enables the identification of road signs and extracts their design, symbols, and text, which often have region-specific characteristics. The system analyses detected signs to provide interpretations that may offer geographic insights, helping investigators assess their relevance to a specific location.

Figure 2. Traffic signs detection
AI-based Indoor Geolocation: Inferring Locations from Interior Features
Indoor geolocation presents additional complexities compared to the outdoor geolocalisation, since indoor scenes lack obvious geographic indicators. Therefore, our AI-based framework (Figure 3) examines various information, including construction materials, architectural features, and furniture patterns to infer locations. It also employs advanced models to generate interpretable predictions, assisting law enforcement with important insights for identifying possible trafficking locations.
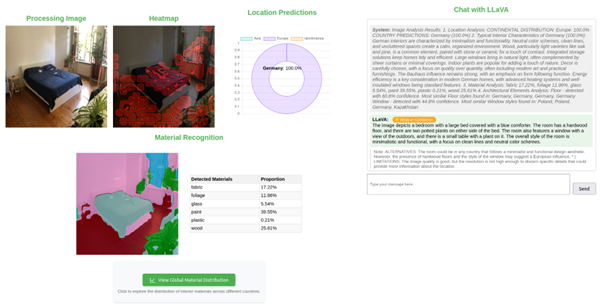
Figure 3. Overview of the Indoors Geolocalisation Framework
The key components of the VANGUARD AI-based Indoor Geolocation tool are presented next.
Deep Hashing for Indoors Geolocalisation: The system employs a deep hashing-based geolocation model, which encodes indoor images and matches them against a global database of listings with known locations. Using a retrieval-based approach, it efficiently infers the most likely geographic origin by identifying the closest matches within the database. Currently, the system can classify indoor images across 14 countries from Europe, Latin America, and Asia.
Architectural Feature Segmentation: A deep learning-based segmentation model identifies key elements such as doors, windows, ceiling structure, and others. The system cross-checks indoor scenes against segmentation databases of doors, windows, floors, and other architectural elements to find the most similar matches per country (Figure 4).
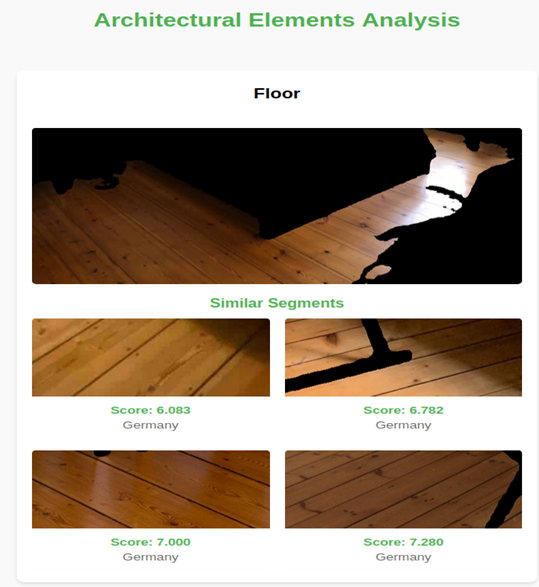
Figure 4. Floor segmentation and retrieval of the most similar match from our database.
Material Recognition & Structural Analysis: AI-based models analyse flooring, ceiling textures, and wall materials to detect specific construction materials in an image. The system provides per-country material statistics, helping investigators check regional distributions and assess the likelihood of a material combination for a given location.
By integrating these AI-powered methods, our framework empowers law enforcement with actionable insights, helping them narrow down potential trafficking locations.
Next Steps
While the already developed solutions mark a significant step forward in AI-based geolocation, continuous improvements are underway. Our next steps will focus on:
- Expanding Indoor Geolocation Coverage: Increasing the number of supported countries, ensuring broader applicability across diverse geographic regions.
- Strengthening the Correlation between Outdoor Visual Cues and Locations: Moving beyond detection by establishing stronger links between extracted visual cues (e.g., signs, license plates, and architectural elements) and potential locations.
As we refine our geolocation frameworks, we are also working on improving interpretability to help users understand potential limitations, particularly regarding regional biases and data representation. Enhancing VLLM’s ability to highlight uncertainties and cultural variations will support more informed decision-making. By integrating AI-driven geolocation into investigative workflows, VANGUARD will consistently contribute to global efforts aimed at combating THB and enhance victim identification.
